A well-placed and properly maintained fire extinguisher can make all the difference during a small fire incident. We offer a wide range of fire extinguishers suitable for various types of fires. Our team ensures that all extinguishers are strategically positioned and regularly serviced, so they are always ready for use. We provide full fire extinguisher services including sales, replacement, and maintenance for all types of extinguishers and cabinets. We also offer training on the proper use of fire extinguishers.
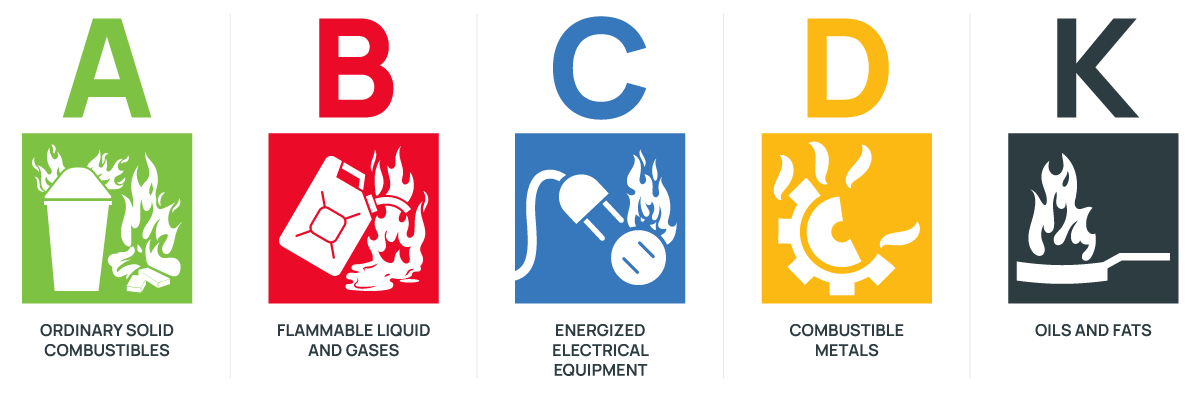
Types of Fires
Fire extinguishers are designed to fight different types of fires. This class system categorizes the appropriate extinguisher for a particular kind of burning material.
Class A: Common Combustibles
Trash, Wood, Paper, Plastic, Cloth
Class B: Liquids
Gasoline, Kerosene, Oil, Propane, Paint
Class C: Electrical Equipment
Computers, Fax Machines
Class D: Combustible Metals
Magnesium, Lithium, Titanium
Class K: Cooking Media
Cooking Oils and Fats
< Read Less
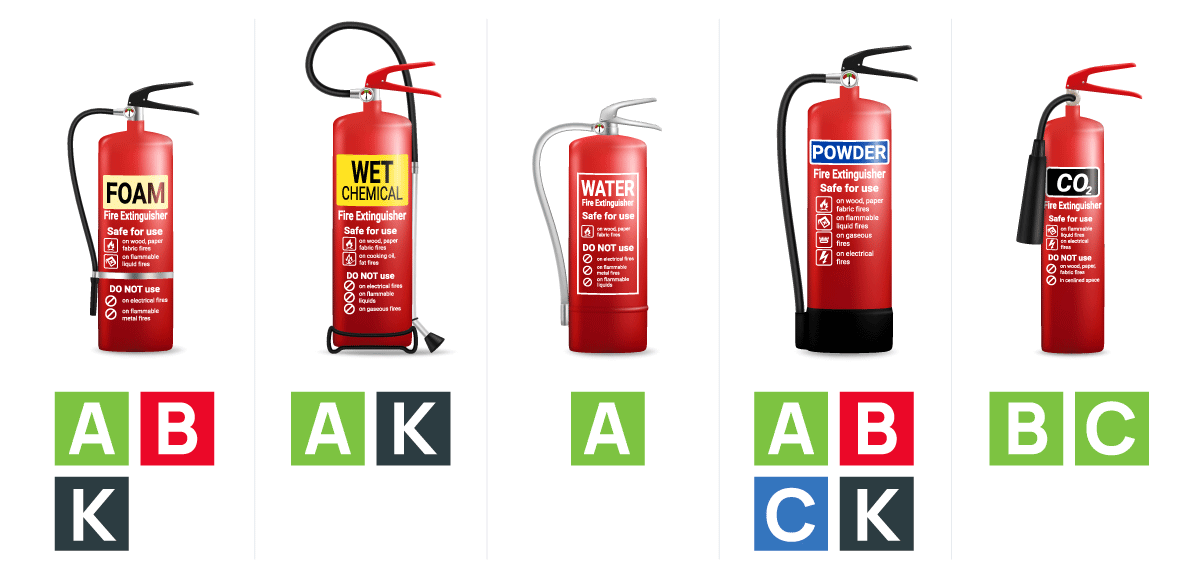
Types of Fire Extinguishers
Water and Foam
These extinguish the fire by taking away the heat. Foam effectively separates oxygen from other elements in the fire. Water extinguishers should only be used for Class A fires.
Carbon Dioxide
These fire extinguishers extinguish fire by taking away the oxygen and removing the heat with a very cold discharge. Carbon dioxide extinguishers are effective for Class B and C fires.
Dry Chemical
This is the most widely used type today. They extinguish the fire primarily by interrupting the chemical reaction of the fire. The multipurpose dry chemical extinguisher can be used for Class A, B, and C fires.
Wet Chemical
This is a new agent that extinguishes the fire by removing the heat and preventing re-ignition by creating a barrier between the oxygen and fuel. This extinguisher was designed especially for Class K fires in commercial kitchens.
Halogenated or Clean Agent
These extinguishers include the halon agents as well as the newer and less ozone depleting halocarbon agents. They extinguish the fire by interrupting the chemical reaction of the fire. Clean agent extinguishers are designed mostly for Class B and C fires.
Dry Powder
These extinguishers are similar to dry chemical except that they extinguish the fire by separating the fuel from the oxygen or by removing the heat of the fire. Dry powder extinguishers are only for Class D fires.
Water Mist
These extinguishers are a recent development that extinguish the fire by taking away the heat element of the fire. They are an alternative to the clean agent extinguishers where contamination is a concern. Water mist extinguishers are intended for Class A fires, and can also be used for Class C fires.
Cartridge Operated Dry Chemical
These fire extinguishers extinguish the fire primarily by interrupting the chemical reaction. A multipurpose dry chemical extinguisher can be used for Class A, B, and C fires; an ordinary dry chemical extinguisher should only be used for Class B and C fires.